Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- QueryDSL
- 그리디
- 인프런
- Servlet
- JDBC
- SpringBoot
- springdatajpa
- 스프링 핵심 기능
- http
- JPQL
- 백준
- 스프링
- transaction
- pointcut
- 스프링 핵심 원리
- Thymeleaf
- Android
- kotlin
- Proxy
- AOP
- Spring Boot
- jpa
- db
- 자바
- spring
- Exception
- 김영한
- java
- Greedy
- 알고리즘
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발자되기 프로젝트
DataInput(Output)Stream, Serialization(직렬화) 본문
1. DataInputStream과 DataOutputStream
- 자료가 메모리에 저장된 상태 그대로 읽거나 쓰는 스트림
- DataInputStream 메서드
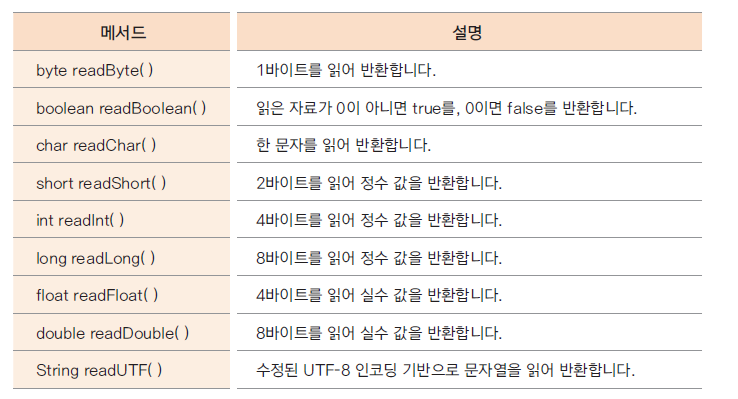
- DataOutputStream 메서드

public class DataStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("data.txt");
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(fos))
{
dos.writeByte(100);
dos.writeChar('A');
dos.writeInt(10);
dos.writeFloat(3.14f);
dos.writeUTF("Test");
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try(FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data.txt");
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(fis))
{
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2. 직렬화(Serialization)
- 인스턴스의 상태를 그대로 파일에 저장하거나 네트워크로 전송(Serialization)하고
이를 다시 복원(Deserialization)하는 방식 - 즉 객체의 정보를 byte Stream의 연속으로 만들고 복원하는 방식
- 자바에서는 보조 스트림을 활용하여 직렬화는 제공
- ObjectInputStream과 ObjectOutputStream
| 생성자 | 설명 |
| ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) | InputStream을 생성자의 매개변수로 받아 ObjectInputStream을 생성합니다. |
| ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) | OutputStream을 생성자의 매개변수로 받아 ObjectOutputStream을 생성합니다. |
3. Serialization 인터페이스
- 직렬화는 인스턴스의 내용이 외부로 유출되는 것이므로 프로그래머가 해당 객체에 대한 직렬화 의도를 표시해야.
- 해당 클래스가 Serializable인터페이스를 구현하도록 함.
- 구현 코드가 없는 marker interface
- transient: 직렬화 하지 않으려는 멤버 변수에 사용함 (Socket등 직렬화 할 수 없는 객체)
- transient가 붙은 멤버 변수는 Serialization에 반영되지 않음.
class Person implements Serializable{
String name;
transient String job;
public Person(String name, String job) {
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class SerializationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person personA = new Person("A", "대표");
Person personB = new Person("B", "사원");
System.out.println("객체 write");
try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("serial.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos)){
oos.writeObject(personA);
oos.writeObject(personB);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("===========================================");
System.out.println("객체 read");
try(FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("serial.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fos)){
Person pA = (Person) ois.readObject();
Person pB = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(pA.toString());
System.out.println(pB.toString());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}- 실행 결과
- job의 경우 transient로 serialization 시 반영되지 않는다.
- 따라서 write.Object()시 job은 null로 들어간다.
객체 write
===========================================
객체 read
Person{name='A', job='null'}
Person{name='B', job='null'}
4. Externalizable 인터페이스
- writeExternal()과 readExternal()메서드를 구현해야 함
- 프로그래머가 직접 객체를 읽고 쓰는 코드를 구현할 수 있음.
class Person implements Externalizable{
String name;
String job;
public Person(String name, String job) {
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
}
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput obj) throws IOException {
obj.writeUTF(name);
obj.writeUTF(job);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput obj) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String name = obj.readUTF();
String job = obj.readUTF();
}
}
public class SerializationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person personA = new Person("A", "대표");
Person personB = new Person("B", "사원");
System.out.println("객체 write");
try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("serial.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos)){
oos.writeObject(personA);
oos.writeObject(personB);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("===========================================");
System.out.println("객체 read");
try(FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("serial.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fos)){
Person pA = (Person) ois.readObject();
Person pB = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(pA.toString());
System.out.println(pB.toString());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5. GitHub : 211031 Serialization
GitHub - bsh6463/various_functions
Contribute to bsh6463/various_functions development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
'Java > 다양한 기능' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Decorator Pattern 예제 (0) | 2021.11.01 |
|---|---|
| 여러가지 입출력 클래스 (0) | 2021.10.31 |
| 보조 스트림 (0) | 2021.10.31 |
| 문자단위 입출력 스트림 (0) | 2021.10.31 |
| 바이트 단위 출력 스트림 (0) | 2021.10.31 |
Comments



