Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- springdatajpa
- Greedy
- 스프링
- JPQL
- java
- QueryDSL
- http
- Servlet
- Android
- 알고리즘
- 김영한
- AOP
- jpa
- Spring Boot
- 인프런
- 백준
- 그리디
- kotlin
- JDBC
- db
- pointcut
- 스프링 핵심 기능
- 자바
- Proxy
- transaction
- SpringBoot
- 스프링 핵심 원리
- Thymeleaf
- spring
- Exception
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발자되기 프로젝트
평균 수행시간이 O(logN)인 알고리즘 : Heap 정렬 & element 삭제 본문
1. Element 삭제하기
루트에 있는 값(별)은, min heap일 때 제일 작고, max heap일 경우 가장 크다.
즉 heap에서 꺼낼 경우 루트에 있는 요소만 꺼낸다.

2. 10을 꺼냈다. 빈칸으로 남는다.

3. 빈칸에는 가장 마지막에 있는 요소가 들어온다고 가정하자.
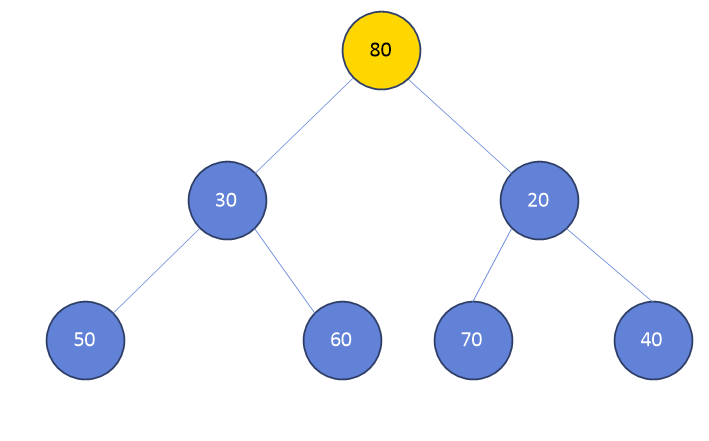
4. 이 때, 80이 저 위치에 있는게 맞냐?!
min heap인 경우 child 중 가장 작은 수와 비교하고. max heap인 경우 child중 가장 큰 수와 비교한다.
지금은 min heap이니 80과 20을 비교한다.

5. 80은 20보다 크다.
80이 기존 20의 자리에 있다고 가정하자!

6. child 중 가장 작은 수인 40과 비교하자.

7. 80은 40보다 크다.
80이 기존 40의 위치에 있다고 가정하자!

8. 정렬 끝!
더 이상 할게 없다! 끝!

위와 같이 위치를 잡아줄 때 검색해야 하는 범위가 단계를 거치면서 1/2씩 줄어든다. 즉 O(log2(N))이다.
9. 코드로 구현하기 : deleteHeap
element를 추가하는 것과 마찬가지고, max heap의 경우 조건을 반대로 변경하면 된다.
public class HeapSort2 {
private int[] heapArry;
int i = 1;
public HeapSort2(){
heapArry = new int [50];
}
public void insertHeap(int input){
heapArry[i] = input;
int index =i;
i++;
int temp = 0;
//parent랑 비교해야함.
while(heapArry[(index/2)] > heapArry[index] && index > 1){ // Min Heap
//while(heapArry[(index/2)] < heapArry[index] && index > 1){ //Max Heap
temp = heapArry[index];
heapArry[index] = heapArry[(index/2)];
heapArry[(index/2)] = temp;
index = index/2;
}
}
public void deleteHeap() {
int parent = 1;
int child = 2;
int temp;
int out = heapArry[1]; //루트에 있는 값을 뺀다.
System.out.println(out + "를 뺀다!");
//heapArry[parent] = heapArry[i-1];
temp = heapArry[i - 1];
heapArry[i - 1] = 0;
i--; //요소 1개 삭제
while (child < getHeapSize()) {
if (heapArry[child] < heapArry[child + 1]) {
child++;
if (temp <= heapArry[child]) break;
heapArry[parent] = heapArry[child];
parent = child;
child = child * 2;
}
}
heapArry[parent] = temp;
}
public void getHeapHeight(){
int height = (int) ((Math.log10(i-1))/(Math.log10(2)))+1;
System.out.println("heap의 height : " + height);
}
public int getHeapSize(){
int size = i-1;
//System.out.println("heap size : " + size);
return size;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeapSort2 heapSort = new HeapSort2();
heapSort.insertHeap(10);
heapSort.insertHeap(30);
heapSort.insertHeap(20);
heapSort.insertHeap(50);
heapSort.insertHeap(60);
heapSort.insertHeap(70);
heapSort.insertHeap(40);
heapSort.insertHeap(80);
System.out.println("Heap : " + Arrays.toString(heapSort.heapArry));
heapSort.insertHeap(7);
//System.out.println("7 추가!");
System.out.println("Heap : " + Arrays.toString(heapSort.heapArry));
heapSort.getHeapHeight();
System.out.println("heap size : " + heapSort.getHeapSize());
System.out.println("요소를 하나씩 빼보자.");
heapSort.deleteHeap();
System.out.println("Heap : " + Arrays.toString(heapSort.heapArry));
System.out.println("heap size : " + heapSort.getHeapSize());
heapSort.getHeapHeight();
}
}
실행 결과이다!
Heap : [0, 10, 30, 20, 50, 60, 70, 40, 80, 0, ...., 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Heap : [0, 7, 10, 20, 30, 60, 70, 40, 80, 50, ...., 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
heap의 height : 4
heap size : 9
요소를 하나씩 빼보자.
7를 뺀다!
Heap : [0, 10, 30, 20, 50, 60, 70, 40, 80, 0, ..... , 0, 0, 0]
heap size : 8
heap의 height : 4'Java > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DFS(Depth - Fist Search) : 코드로 구현 (0) | 2021.06.04 |
|---|---|
| DFS(Depth - Fist Search) : 개념, 예시 (0) | 2021.06.04 |
| 평균 수행시간이 O(logN)인 알고리즘 : Heap 정렬 & element 추가 (0) | 2021.06.01 |
| 평균 수행시간이 O(n^2)인 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.05.31 |
| 정렬된 수 에서 특정 수의 위치 찾기 : binary search (0) | 2021.05.31 |
Comments




